Air Quality
Air Pollution Control
Brief Introduction
The area of New Taipei City totals 2,053 km2. As the largest county in the nation, New Taipei City has the largest population, and the largest numbers of motor vehicles, factories, and construction sites nationwide. The air quality in New Taipei City, therefore, is heavily influenced by these various types of pollution source.
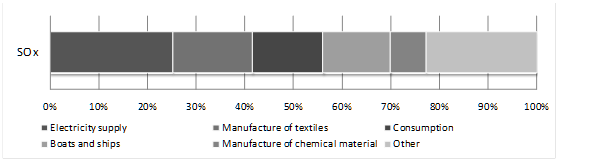
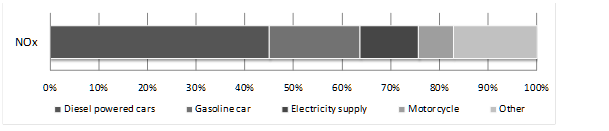
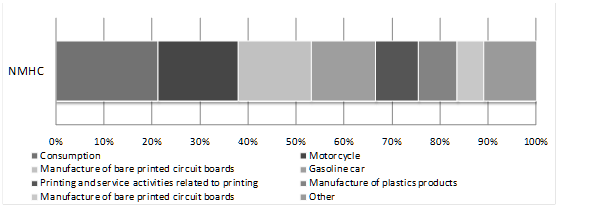
According to National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS), the main air pollutants are: Particulate Matter under 10 microns (PM10), Sulfur Oxide (SOx), Nitrogen Oxide (NOx), Non-Methane Hydrocarbons (NMHC). Their yearly emissions are depicted in Graph.
In addition, increasing Ozone (O3) is another important problem New Taipei City currently face. Tightening control of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pollutions from oil stations, restaurants, motor vehicles, open burnings and other organic solvents related business is therefore the key objective that DEP will be working on soon.Graph 1.1 Yearly Emissions of Pollution Sources in New Taipei City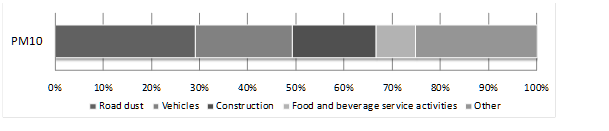
I. Stationary Source
Key Regulation Works
1.Tighten control of pollution sources.
A. Randomly inspect chimneys with negative records.
B. Periodically inspect operations of certified pollution prevention equipments to ensure pollution prevention efficiency.
2.Emission reduction and seasonal annual repairs.
- Supervise on emission reduction and suggest factories with large boilers to process annual repairs during spring and summer.
3.Collect air pollution prevention fees to be used in related protection works.
4.Supervise and evaluate volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pollution management.
5.Periodically monitor, inspect, and document the status of pollution sources.
6.Inspect oil gas recycle systems and operations of oil stations.
7.Regulate and provide guidance to restaurant business.
8.Implement an emission reporting system.
9.Target-oriented regulations on continuous automatic monitoring systems.
10.Tighten control of DIOXIN emission from refuse incineration plants.
II. Mobile Source
1.Evaluate emissions from mobile source.
A. Implement roadside emission inspection programs for motorcycles and motor vehicle emission remote monitoring systems.
B. Implement a citizen reporting system to effectively report high-pollution vehicles.
Randomly select and inspect possible high-pollution vehicles through eye measurement and effectively track the improvement records.
2.Improve motorcycle inspection rate.
- Effectively improve motorcycle inspection rate through roadside inspections and various promotional and educational programs.
3.Promote the EPA policy of replacing older motor vehicles.
4.Tackle down the use and sale of illegal oil products.
5.Improve the transportation system.
A. Implement reversible lanes and prohibit roadside parking during traffic peak time.
B. Establish computerized traffic signal systems to reduce waiting time.
C. Encourage the use of public transportation system and the Metro Rapid Transit.
III. Fugitive Area Source- Tighten inspection on construction sites and implement the “Regulations on Air Pollution Prevention Equipments in Construction Sites” (RAPPECS).
- Closely control and regulate the construction of routing and piping systems and other key construction details.
- Promote the Adopt-A-Road program to reduce road dust through regular street cleaning funded by private business or construction companies.
- Collect air pollution prevention fees in construction sites.
- Conduct street cleaning to reduce road dust.
- Afforest wastelands.
In accordance with Kyoto Protocol, DEP is to effectively control and regulate greenhouse gases emission and draft emission reduction strategies and policies.
Noise Control
Brief Introduction
The existing environmental and road traffic noise monitoring systems in New Taipei City can be categorized into manual and automatic systems. There are 13 manual environmental and 10 road traffic noise monitoring stations, and 2 automatic road traffic noise detection stations.
Key Regulation Works
1.Reinforce related legislations.
A. Promulgate the prohibition of noise producing and other peace disturbing activities.
B. Promulgate noise control restrictions in nonprofit facilities.
2.Increase control and monitoring of stationary sources and road traffic noise. Track the improvement records.
3.Tighten restrictions on noise from cultural and neighborhood activities.
4.Review noise control zones.
A. Re-plan and promulgate noise control zones in New Taipei City.
B. Promulgate noise control zones (for territories under New Taipei City jurisdiction) in Chiang Kai-Shek Airport, Taipei Songshan Airport, and Taoyuan Military Airport.
6.Establish a major noise and vibration control and prevention mechanism.
Future Vision
In accordance with “National Environmental Protection Plan” (NEPP), the future goals for noise pollution control in New Taipei City are as follows:
Type Indicator Moving Average Targets2008 Targets2012 Targets2017 Noise Percentage of noise level over the environmental standard in common areas(%) 48.81 <30 <20 <10
Lin,Chin-Chia TEL: 2953-2111 Ext.3282